[無料ダウンロード! √] tensile yield stress formula 125776-Tensile yield stress formula
Tensile strength It is defined as force per unit area which is associated with stretching and denoted by σ It is defined as the amount of tensile stress a material can withstand before breaking and denoted by s The formula is σ = F/A Where, σ is the tensile stress;Tensile strength is usually of a higher numerical value than the yield strength of aIf the force is acting perpendicular to the surface is given by F, and the surface area is H, then tensile stress (T) is given by T = F / H SI unit of T = Pascal (Pa) or Newton per meter square or N x m ^ 2 Dimensional formula for tensile stress = M ^ 1 L ^ 1 T ^ 2
Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
Tensile yield stress formula
Tensile yield stress formula-Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimateAllowable Stress (Strength) The allowable stress or allowable strength is the maximum stress (tensile, compressive or bending) that is allowed to be applied on a structural material The allowable stresses are generally defined by building codes, and for steel, and aluminum is a fraction of their yield stress (strength)


Stress Strain Tensile Stress Tensile Strain Elastic Strain Energy Breaking Stress Plastic Brittle
If the force is acting perpendicular to the surface is given by F, and the surface area is H, then tensile stress (T) is given by T = F / H SI unit of T = Pascal (Pa) or Newton per meter square or N x m ^ 2The difference is in the directions of forces For the case on the shown on the diagram, the top face of the object gets displaced relative to the bottom face of the objectAllowable Stress (Strength) The allowable stress or allowable strength is the maximum stress (tensile, compressive or bending) that is allowed to be applied on a structural material The allowable stresses are generally defined by building codes, and for steel, and aluminum is a fraction of their yield stress (strength)
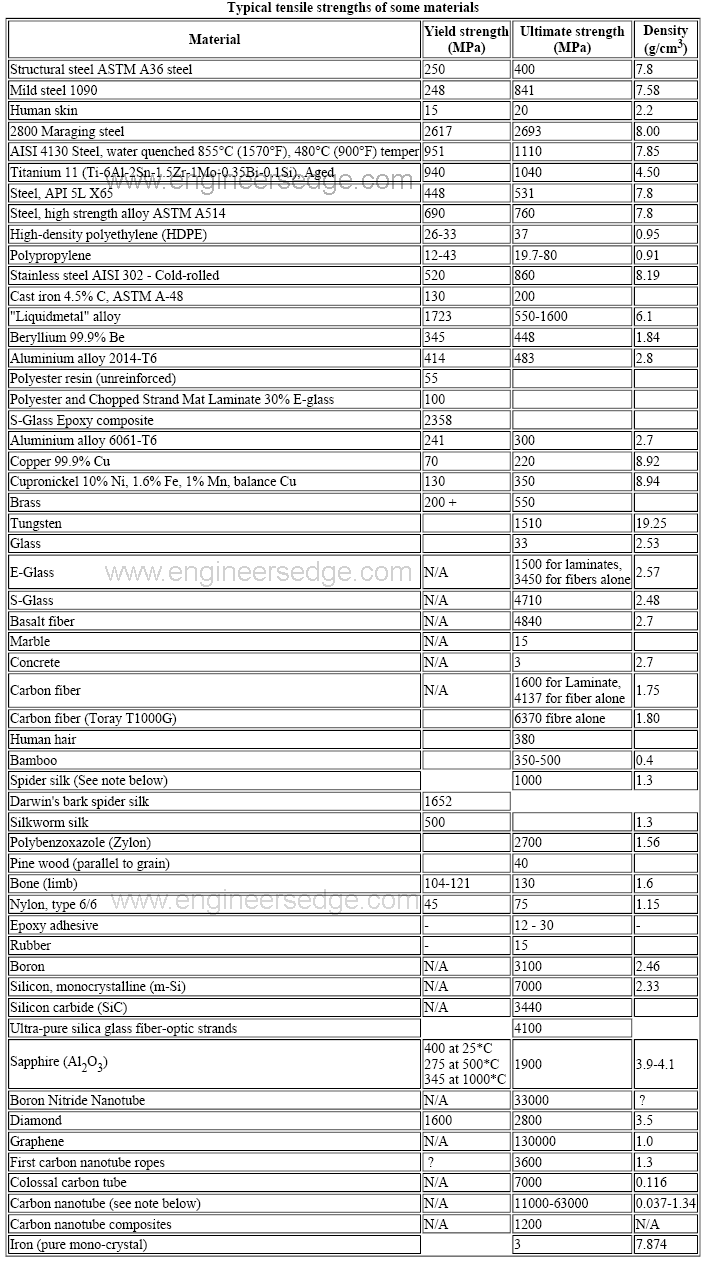
Effective length 5 inches;The ductile strain ε is communicated as ε = ΔL/L In the event that a concrete compressive tensile force is applied, the concrete compressive strain is communicated as ε = ΔL/L In view of Hooke's law, the connection among anxiety is communicated as σ = Eε, where σ stress, E Young's modulus and ε strainThis assumes that yield occurs when the shear stress exceeds the shear yield strength τ = σ 1 − σ 3 2 ≤ τ y {\displaystyle \tau ={\frac {\sigma _{1}\sigma _{3}}{2}}\leq \tau _{y}\,\!} Total strain energy theory – This theory assumes that the stored energy associated with elastic deformation at the point of yield is independent of the specific stress tensor
In these two diagrams the stress and strain are defined as given below Stress = Force/Original area of crosssection of specimenMaterials shall adhere asrm yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation of 65 ksi and maximum yieldtotensile strength ratio of 0 in Tension (E) x 10 6 psi in Shear, in terms of E 0 255 117 This is a list of ASTM International standards 097 in 81 99This is the minimum requirement for F1554 grade 36


Engarc L Offset Yield Method
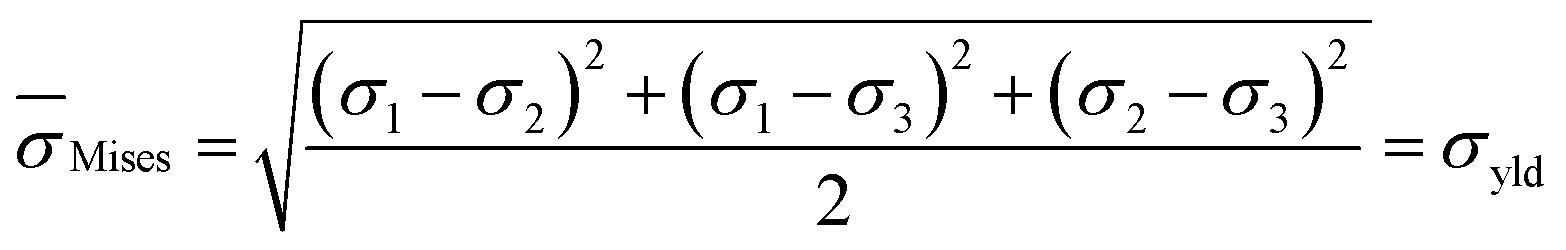


A New Form Of Equivalent Stress For Combined Axial Torsional Loading Considering The Tension Compression Asymmetry Of Polymeric Materials Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing
The tensile strength of concrete is used in combinedstress design In normalweight, normaldensity concrete the tensile strength can be found from Advertisements More Entries Is it desirable to use concrete of very high strength ie exceeding 60MPa?A is the area;Use the following calculator to convert yield or tensile values in ksi, Mpa, N/mm² or psi Type the value in the box next to Mpa (using the drop down to change the unit of measurement) ksi MPa N/mm² psi = ksi MPa N/mm² psi



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University
The formula is Tensile Stress = Force / Cross Sectional Area Tensile Stress Megapascals (Mpa) Force Newtons (N) Cross Sectional Area Square millimeters (mm 2) We have a 4, newton force acting on a 305 Stainless Steel (annealed) wire with a cross sectional area of 3925 mm2This amount of force is the yield strength To test yield strength in our example, you would put our ½13 bolt into the tensile machine, stretch the part until it distends, and calculate the force at the point of yield In this case, the force would need to be a minimum of 18,500 lbf for the part to passWhat are the potential problems associated with such high strength concrete?



How Do You Identify The Elastic Limit And Yield Point On A Stress Strain Graph Physics Stack Exchange



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The formula is s = P/a Where, s is the tensile strengthYield Load(Tons) Ultimate load(Tons) Area of Bar, A=∏ D 2 /4 Yield Strength=Yield Load *24/ Area Tensile Strength = Yield Load*24/ Area 1 ½ in 597 928 0196 in2 Psi 65 Psi 2 ½ in 486 765 0196 in2 Psi 46 Psi 3 ½ in 547 811 0196 in2 Psi 12 Psi 4 ½ in 543 13 0196 in2 Psi 10 Psi 5 1/8 in 705 1095Mathematically the yield function for the von Mises condition is expressed as An alternative form is where k can be shown to be the yield stress of the material in pure shear As it will become evident later in the article, at the onset of yielding, the magnitude of the shear yield stress in pure shear is √3 times lower than the tensile yield stress in the case of simple tension


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables


Http Web Mit Edu Dlizardo Www Uniaxialtestinglabreportv6 Pdf
The definition of stress that takes the continuous change in the area into account is called true stress Difference between Yield Strength and Tensile Strength Definition Yield strength is the stress that causes a material to lose its elastic behaviour Tensile strength is the maximum stress that a material can handle before breakingTensile stress area in bolts according ISO 81 Mechanical properties of fasteners made of carbon steel and alloy steel As,nom = (π / 4) ((d2 d3)/ 2)2 (2)Tensile strength of steel will show us how much tensile stress the steel can withstand until it leads to failure in two ways ductile or brittle failure Ductile failure – think of this as the preliminary stage of failure, where it is pushed beyond the yield point to permanent deformation


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics


Tensile Testing Alex S Web Page
F is the force acting;S = Breaking Strength (stress) F = Force that Caused the Failure A = Least Cross sectional Area of the Material Using the above Ultimate tensile strength formula, the UTS can be calculated by dividing the load or force at break and the original minimum crosssectional areaProof load, yield strength, and tensile strength are numbers set by a standard that a fastener must meet in order to qualify as a certain grade or property class All three numbers are set as minimum (and occasionally maximum) values For example, according to ASTM A354, in order for a ½13 bolt to qualify as grade BD, it must have a minimum



Tensile Strength Of Steel Vs Yield Strength Of Steel Clifton Steel



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
Yield in ductile materials is usually caused by the slippage of crystal planes along the maximum shear stress surface Therefore, a given point in the body is considered safe as long as the maximum shear stress at that point is under the yield shear stress obtained from a uniaxial tensile testS tensile = t min x a Shear Strength of a thread S sy = p r x s yield Where ymin = Minimum Yield of bolt threads engaged (lbs) s yield = Minimum yield strength of the bolt grade, ASTM, SAE, etc (psi) s tensile = Ultimate Yield Strength (lbs) t min = Minimum tensile strength of the bolt grade, ASTM, SAE, etc (psi)Tensile strength It is defined as force per unit area which is associated with stretching and denoted by σ It is defined as the amount of tensile stress a material can withstand before breaking and denoted by s The formula is σ = F/A Where, σ is the tensile stress;



What Is The Difference Between Ultimate Stress And Yield Stress Quora



What Is The Formula For Tensile Strength How Is This Determined Quora
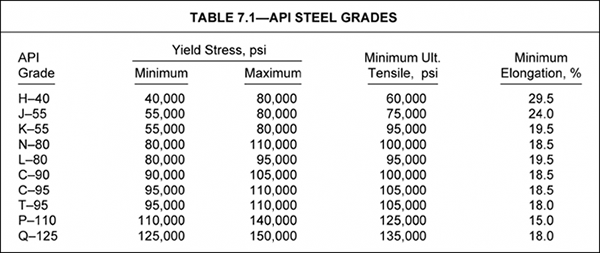
Maximum Yield Strength 95,000 psi Minimum Tensile Strength 95,000 psi Hardness Requirement 23 HRC maximum Notes Manufactured to API specification 5CT This is a controlled yield strength material with a hardness testing requirement L80 is usually used in wells with sour (H2S) environmentsF is the force acting;The tensile strength is calculated by dividing the maximum load by the original crosssectional area of the test specimen Yield Strength;



Ultimate Tensile Strength Importance Testing Examples Fractory


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I
Stress, σ, is defined as the force divided by the initial surface area, σ=F/A o This pulling stress is called tensile stress Strain is what results from this stress Strain, ε, is defined as the change in length divided by the original length, ε = Δ I / I o Before we proceed further with stress and strain, let's define some other typesWhen the elastic limit is exceeded, the curve flattens out as in the stressstrain diagram of the tensile test and indicates the yield force F y With this yield force the induced bending moment M b y = F y ⋅ L S 4 can be determined at the onset of plastic deformation and thus the flexural yield point according to the equation (7)State ν = − ϵ l a t e r a l ϵ a x i a l \nu=\frac {\epsilon_ {lateral}} {\epsilon_ {axial}} Poisson's ratio is sometimes also defined as the ratio of the absolute Absolute Measurement A Measurement made without a direct reference to a second signal or measurement



Yield Strength
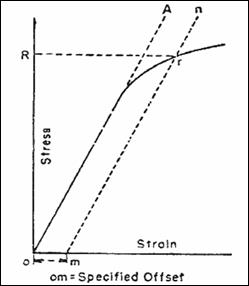


To Determine Yield Strength Tensile Strength Of A Steel Bar By Offset Secant Method
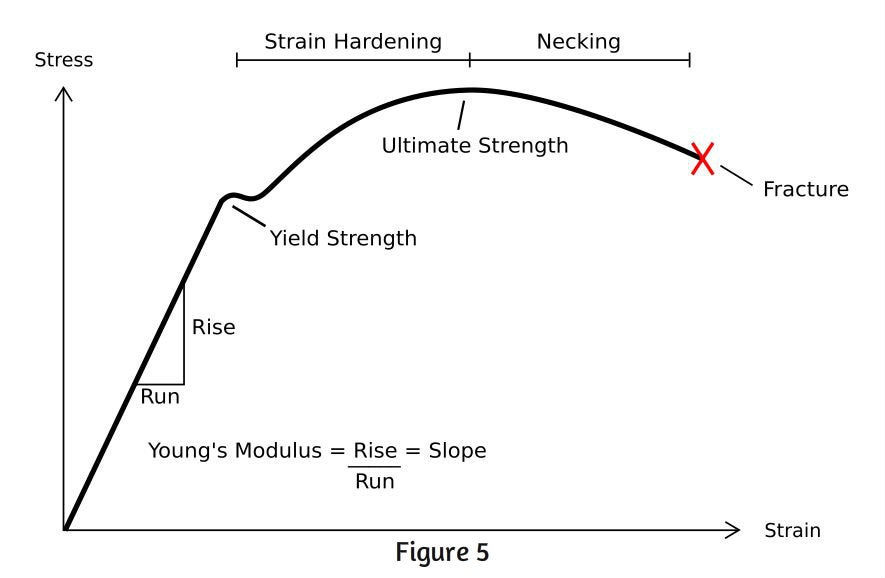
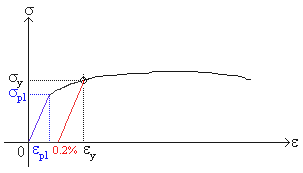
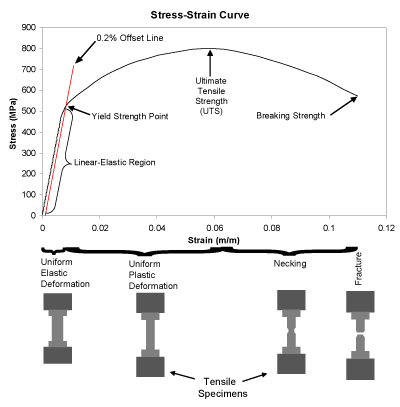
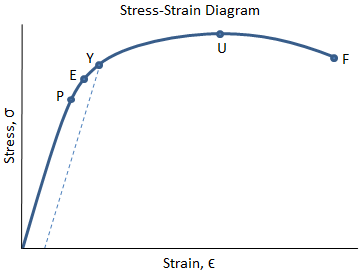
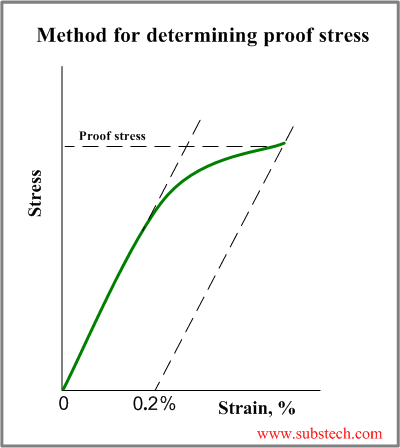
The equation below is used to calculate the stress stress = stress measured in Nm2 or pascals (Pa) F = force in newtons (N) A = crosssectional area in m 2 Strain The ratio of extension to original length is called strain it has no units as it is a ratio of two lengths measured in metres strain = strain it has no units D L =extension measured in metres L = original length measured in metres StressStrain graph for a ductile material (like copper)S = Breaking Strength (stress) F = Force that Caused the Failure A = Least Cross sectional Area of the Material Using the above Ultimate tensile strength formula, the UTS can be calculated by dividing the load or force at break and the original minimum crosssectional areaThe stress corresponding to a specified permanent (plastic) deformation The specified permanent deformation has been standardized in the nonferrous industry as 02% offset on the stressstrain curve Elongation
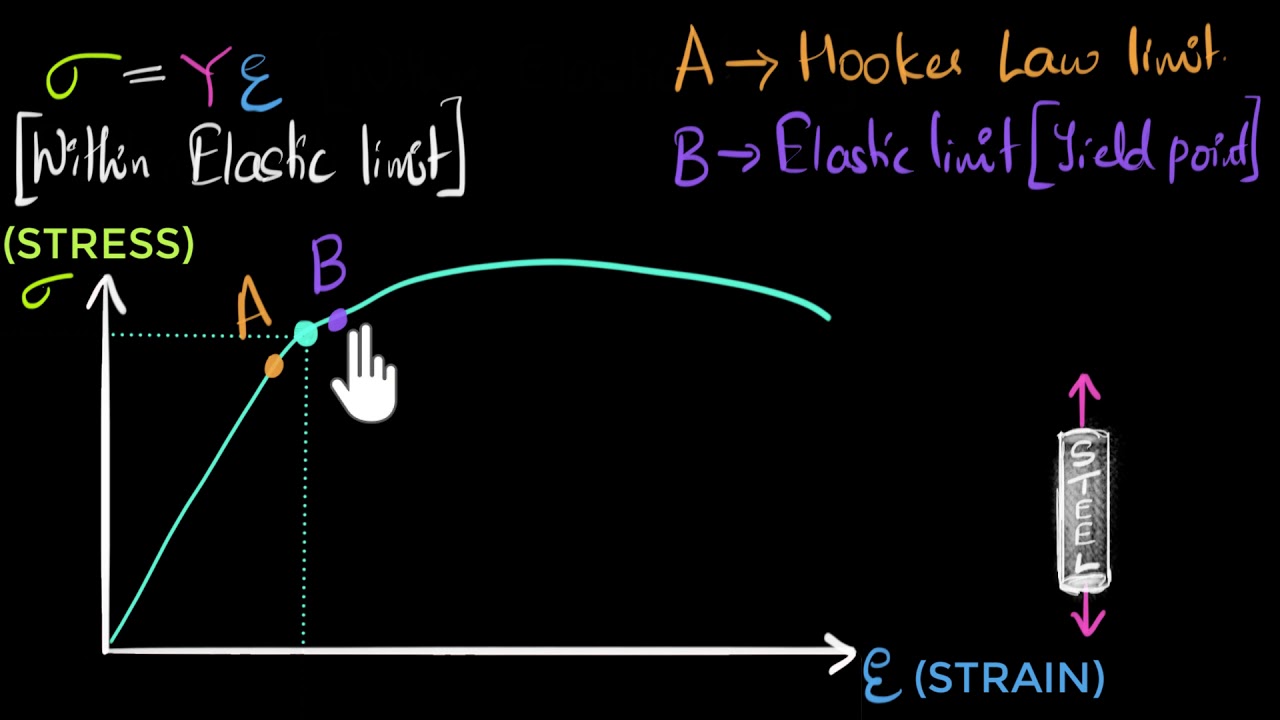


Stress Vs Strain Curve Video Khan Academy



Strength At Break Tensile
Stress Area (A sub S) is the ASSUMED AREA OF AN EXTERNALLY THREADED PART, used for the purpose of computing tensile strength It is given by the formula A sub s = (E sub m K sum m)/4 squared where E sub m = the mean pitch diameter and K sub m = the mean minor diameterDue to the linear stress distribution at a bending load, the flexural yield strength for steels is about 10 % to % higher than the tensile yield strength!Since, Elongation at yield is the deformation of a thermoplastic or thermoset material at this yield point, it is calculated as the relative increase in length Elongation = ɛ = (ΔL/L) x 100 Where
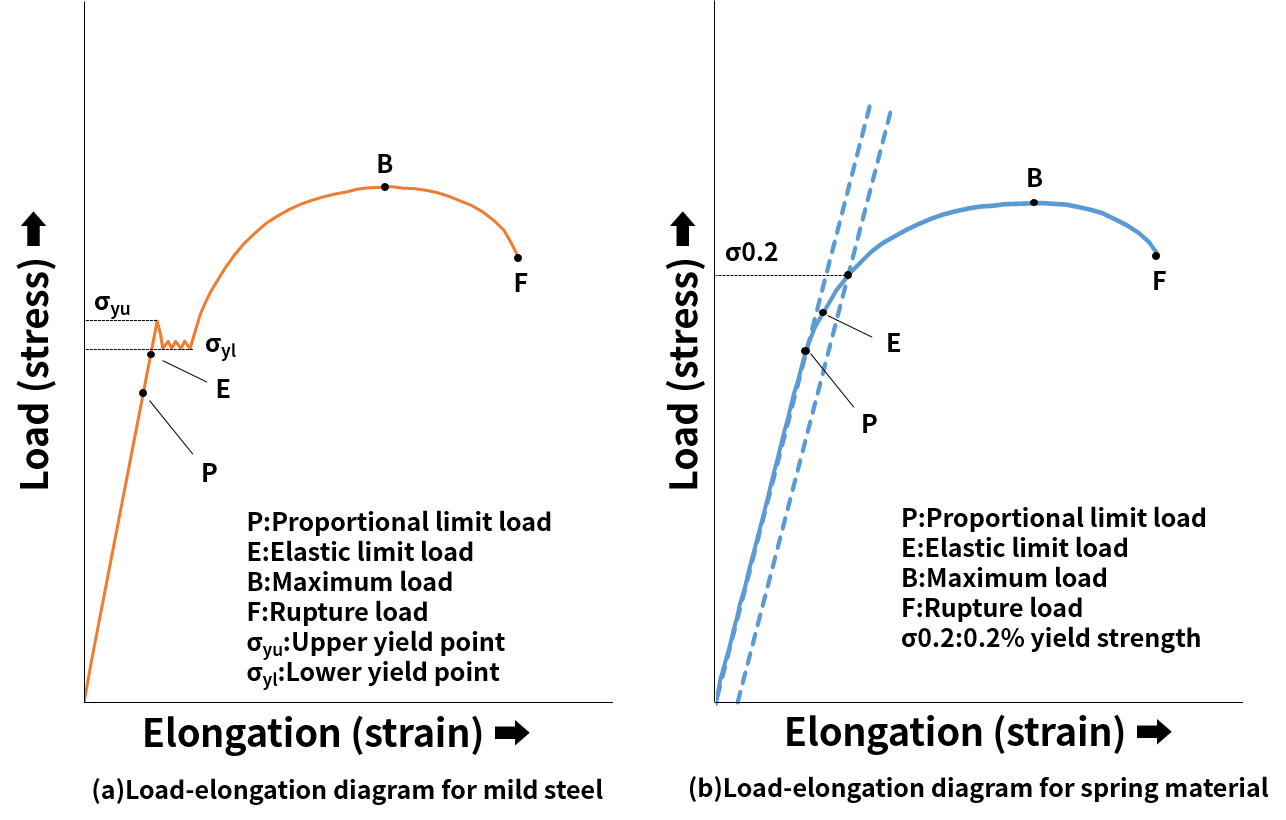


Compression Springs How To Calculate Spring Stress Tokai Spring Industries Inc


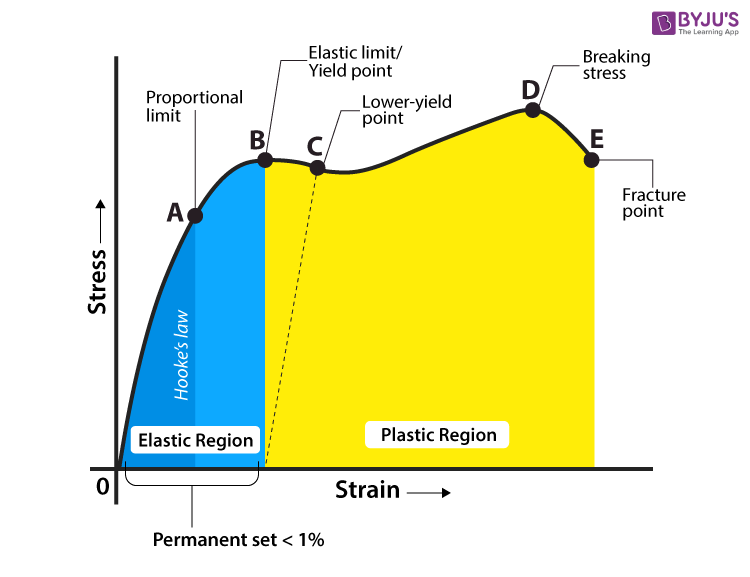
Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
The tensile stress area can be calculated asT 494 om01 Tensile properties of paper and paperboard / 2 (using constant rate of elongation apparatus) 2 Definitions 21 Tensile strength, the maximum tensile force developed in a test specimen before rupture on a tensile test carried to rupture under prescribed conditionsTake the minimum tensile strengthin psi of the ASTM grade, multiplied by the stress areaof the diameter This formula will give you the ultimate tensile strength of that size and grade of bolt ExampleWhat is the ultimate tensile strength of a 3/4″ diameter F1554 Grade 36 rod?



How To Measure Tensile Strength Elastic Modulus And Ductility Rolled Alloys Inc



Isbt212 04 3 Stress And Strain Proportional Limit And Yield Strength Youtube
The definition of stress that takes the continuous change in the area into account is called true stress Difference between Yield Strength and Tensile Strength Definition Yield strength is the stress that causes a material to lose its elastic behaviour Tensile strength is the maximum stress that a material can handle before breakingTensile Stress Tensile stress can be calculated as σ = F / A (3)σ = stress (N/m², lb/in², psi) F = applied force (N, lb) A = stress area of object (m², in²) · tensile stress – stress that tends to stretch or lengthen the material – acts normal to the stressed area · compressible stress – stress that tends to compress or shorten the material – acts normal to the stressed area



Solved B Calculate The 0 2 Offset Yield Stress In Gpa Chegg Com



Ch 2 Stress Strains And Yield Criterion
For materials with no visible yield strengths in the stresscurves, a 02 % flexural offset yield strength \(\sigma_{by02}\) can be defined analog to the 02% offset yield strength of theThe shear stress is again defined as the ratio of the force to the area The definition for tensile stress and shear stress are similar;As yield strength is related to deformation which is a result of applied stress, the SI unit of yield strength is Nm 2 In CGS system, the yield strength is gcm 2 State if the given statement is true or false In drawing deep operations of sheet steels, problems are created by yield point phenomenon



Stress Strain


Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials
The shear stress on this plane when yielding occurs is therefore τ = σ y /2, and we define this as the shear yield strength k Figure 123 In a polycrystalline material the average slip path is at 45° to the tensile axisThread pitch 9;The tensile yield stress of a material is the applied stress required to start plastic deformationof the material under a tensile load We want to relate the tensile stress applied to a sample to the shear stress that acts along the slip direction φ λ σ φ λ φ λ τ cos cos cos cos cos cos _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ = = = =


Stress Strain And Young S Modulus



Stress Strain Diagram Instron
Tensile Stress Tensile stress can be calculated as σ = F / A (3) where σ = tensile stress (psi, N/m 2 (Pa)) Example Bolt Stretching Imperial Units stud diameter 7/8 inches ;The most common engineering approximation for yield stress is the 02 percent offset rule To apply this rule, assume that yield strain is 02 percent, and multiply by Young's Modulus for your material σ = 0 0 0 2 × E \sigma = 0002\times E σ = 0002×EYield strength in such a case is the stress value on the stressstrain curve corresponding to a definite amount of permanent set or strain, usually 01 or 02 per cent of the original dimension Modulus of elasticity Metal deformation is proportional to the imposed loads over a range of loads Ultimate strength (tensile)



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet
Young's Modulus steel 30 10 6 psi;The formula is s = P/a Where, s is the tensile strengthThe forces acting on it are trying to stretch the material Compression is when the forces acting on an object are trying to squash it The equation below is used to calculate the stress stress = stress measured in Nm 2 or pascals (Pa) F = force in newtons (N) A = crosssectional area in m 2


Tesile Property Of Pipe Drilling Formulas And Drilling Calculations



3 1 4 A Bit More About Tensile Testing
A is the area;Tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation really do not have such a numerical relationship that can be applied Some people have tried to relate tensile strength to yield strength as a rule of thumb, but these relationships really vary due to processing including heat treatmentMinimum yield strength 38,000 psi Tensile strength 70,000 psi Allowable stress (70,000/35 = ,000) as per Post Addenda1999 Edition Test pressure 13 × MAWP Determine Hydraulic test pressure Solution Effectively the 13 × MAWP is loading the walls at 13 × ,000 = 26,000 psi during full test pressure, or about 68% of yield strength


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
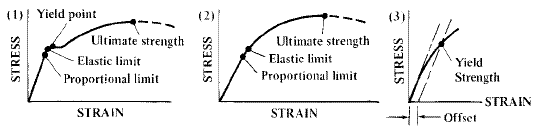


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
Stress Area The tensile stress area can be calculated as A = (π / 4) (d / n) 2 (2) where d = nominal diameter of bolt (in) n = 1 / p = number of threads per inch p = pitch, length per thread (in) nominal bolt stress area according ISO 724;State ν = − ϵ l a t e r a l ϵ a x i a l \nu=\frac {\epsilon_ {lateral}} {\epsilon_ {axial}} Poisson's ratio is sometimes also defined as the ratio of the absolute Absolute Measurement A Measurement made without a direct reference to a second signal or measurementThe yield point happens after an object has reached its yield stress This example is of steel Steel materials have a yield point, which causes them to have a large horizontal portion of the graph



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
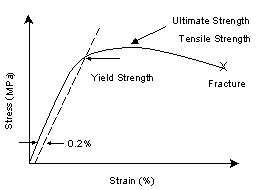


Efatigue Glossary
Designed bolt load lb;



Yield Engineering Wikipedia



Ch 2 Stress Strains And Yield Criterion


Ultimate Shear Stress Formula Drone Fest



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



Calculation Methods Of Yield Strength And Ultimate Tensile Strength By Download Scientific Diagram



Tensile Strength Of Steel Vs Yield Strength Of Steel Clifton Steel


Stress Strain Tensile Stress Tensile Strain Elastic Strain Energy Breaking Stress Plastic Brittle
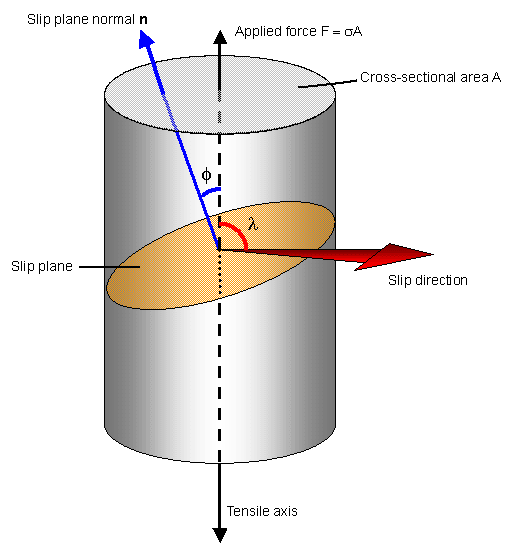


Doitpoms Tlp Library Slip In Single Crystals Slip Geometry
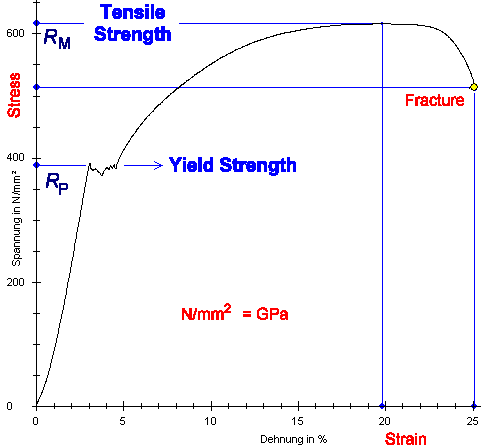


Science Of Uniaxial Deformation


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf



Smts And Allowable Stress Amarine
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods
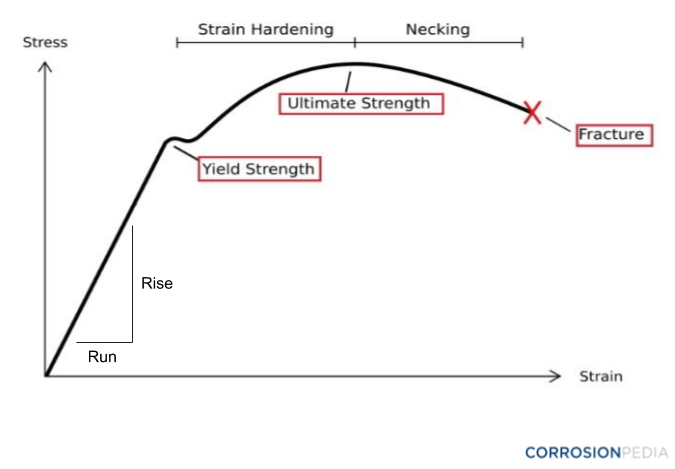


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia



Solved Problem 1 Find The Ultimate Tensile Strength An Chegg Com



What Is The Relation Between Tensile Strength And Young S Modulus Of A Material



How To Find Yield Strength Quora



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv


Engineering Stress Strain Curve
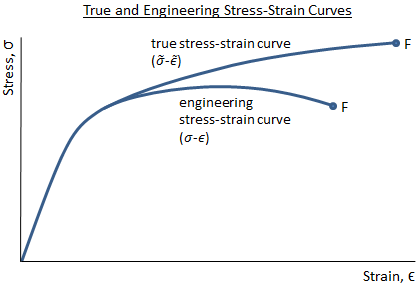


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc


Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve



What Is Tensile Testing Instron



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University



Yield Point Instron



Initial Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Strength At Break Tensile



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
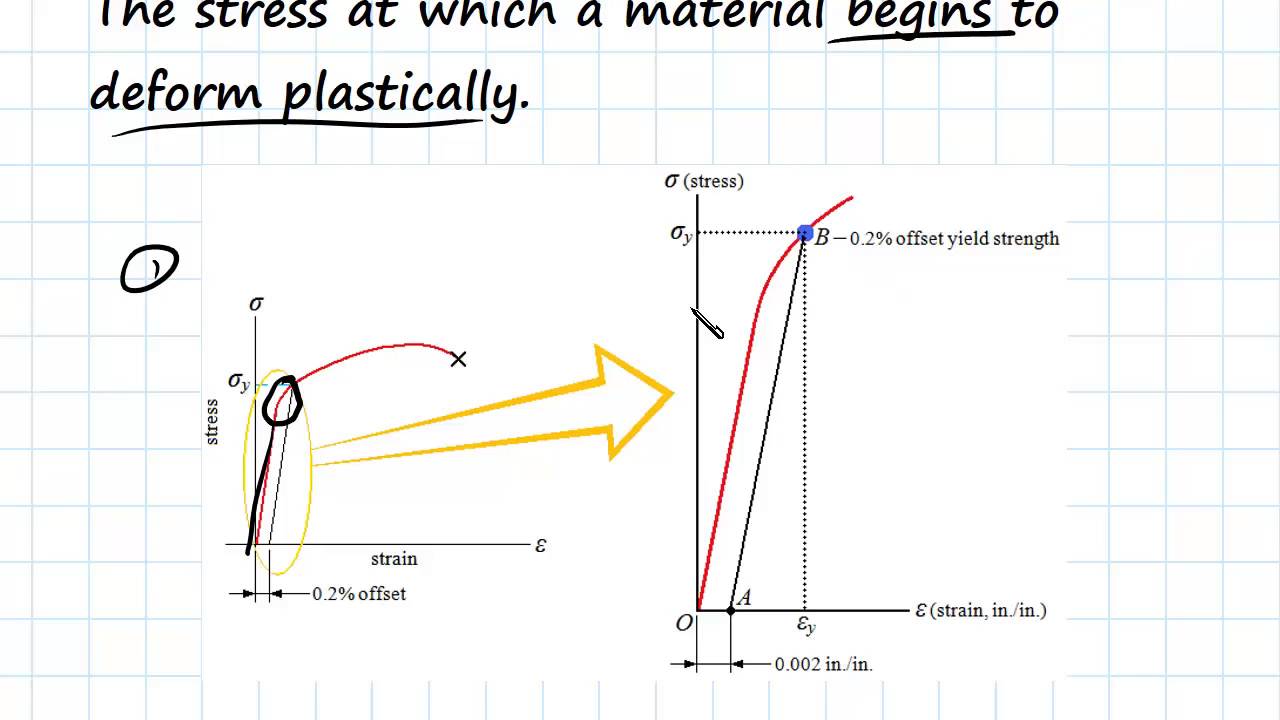


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube


What Is Proof Load Of A Bolt And How Is It Different From Yield Strength Smartbolts
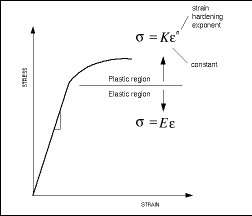


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve


What Are Tensile Strength Units Quora
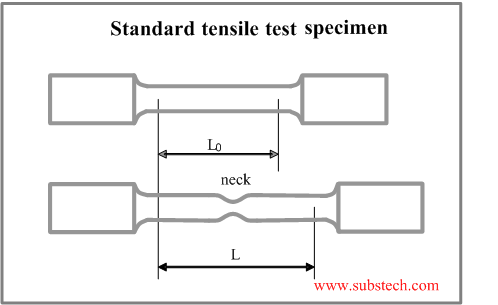


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech


Q Tbn And9gcttwoqta7jtsg 3vilhdf Yhokhwjyvlxmyndyl3ieisjtj3uoc Usqp Cau



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Q Tbn And9gcsubgeg9vwumror Qhoghyyxdjrgpugf4zei Gvjvgk9mt175y Usqp Cau


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot
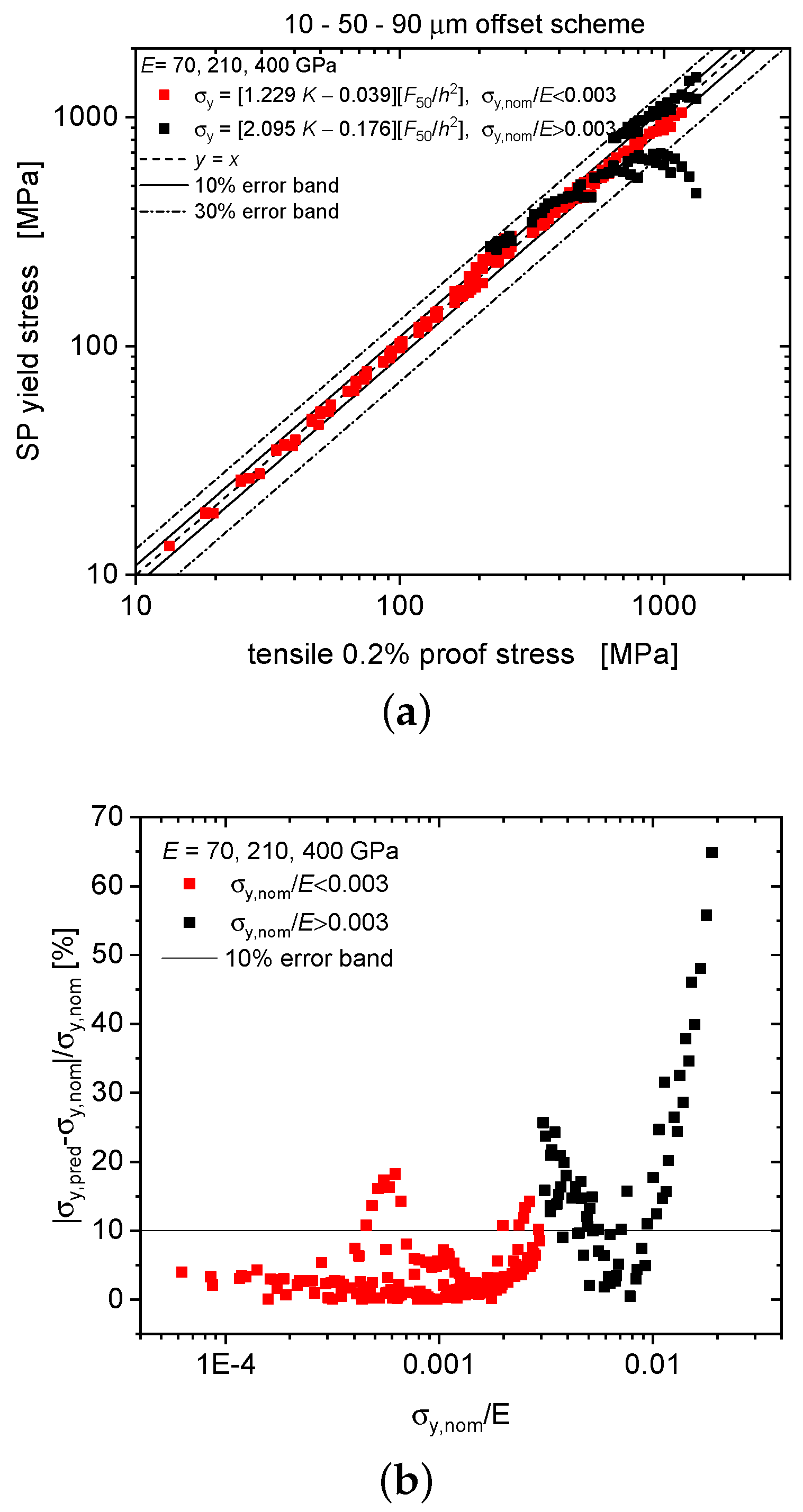


Materials Free Full Text An Enhanced Method To Evaluate Tensile Yield Stress By Small Punch Tests Using Deflection Curves Html


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech


Tensile Yielding
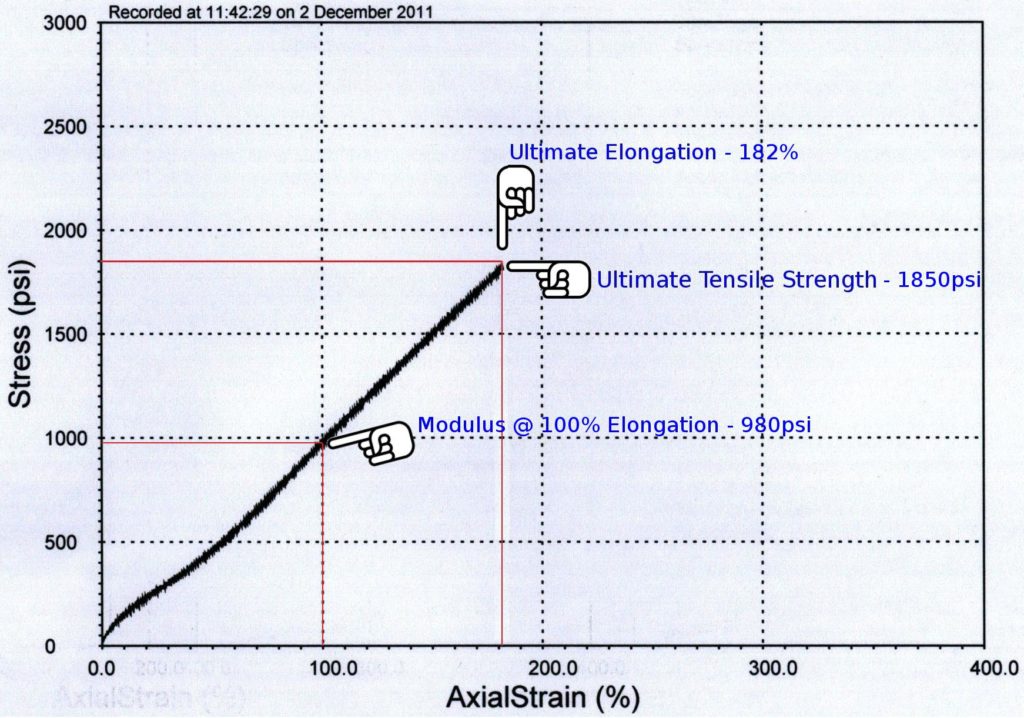


Physical Properties Of Rubber Satori Seal Corporation



Calculation Methods Of Yield Strength And Ultimate Tensile Strength By Download Scientific Diagram


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I



Calculate Yield Stress Youtube


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau



Tensile Yield Stress An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



How To Find Yield Strain Corresponding To 0 2 Offset Yield Stress


Basic Of Drillpipe Tensile Capacity And Its Calculation Drilling Formulas And Drilling Calculations



Strength Of Materials By S K Mondal Pdf By S Dharmaraj Issuu
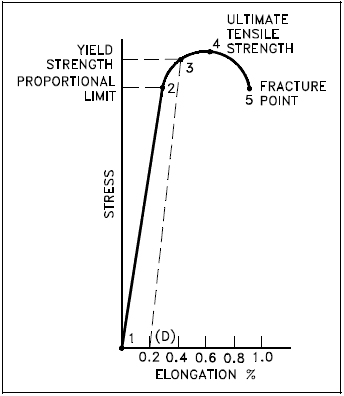


Properties Of Metals Engineering Library
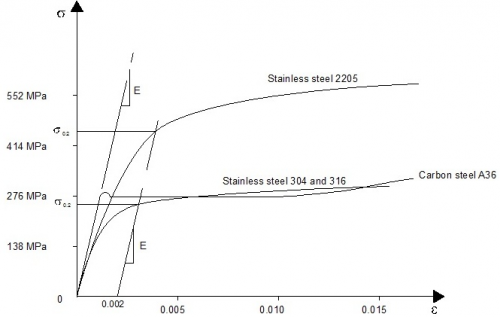


Steel Material Properties Steelconstruction Info
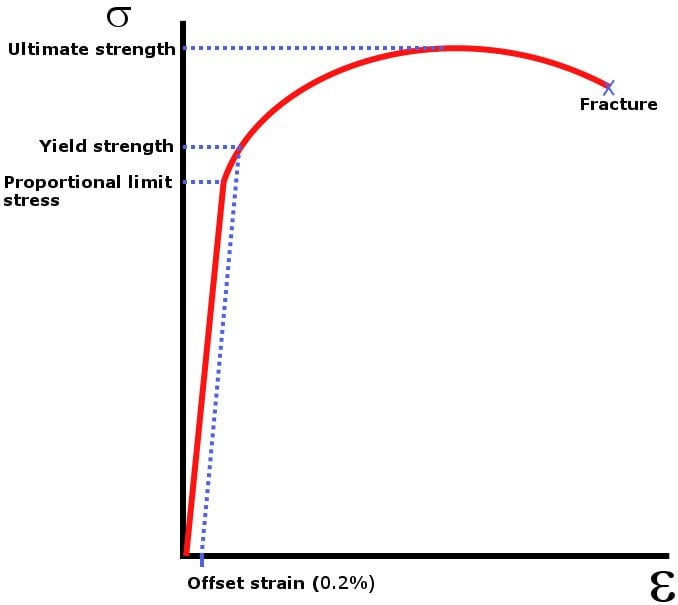


What Is Ultimate Tensile Strength Science Abc



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve
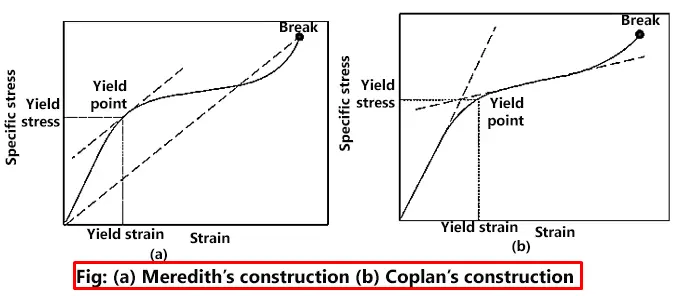


Tensile Testing Terms And Tensile Testing Terms Definitions Textile Study Center



Tensile Properties Torelina Toray Plastics Toray


Stress Strain Tensile Stress Tensile Strain Elastic Strain Energy Breaking Stress Plastic Brittle



Proof Load Yield Strength And Tensile Strength Wilson Garner Company



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Power Law



Solved Problem 1 Find The Ultimate Tensile Strength An Chegg Com


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet



A Comparative Evaluation Of Metallurgical Properties Of Stainless Steel And Tma Archwires With Timolium And Titanium Niobium Archwires An In Vitro Study Vijayalakshmi R D Nagachandran K S Kummi P Jayakumar


Q Tbn And9gcrf0yb4daxmcs4hece0wbtm Gkjp Dgiun5uwt1stzt02mpf2vo Usqp Cau



Allowable Stress In Asme Viii 1 3 Api 650 Api 653 Amarine



Estimating Tensile Strength From Yield Or 0 2 Proof Values Twi


コメント
コメントを投稿